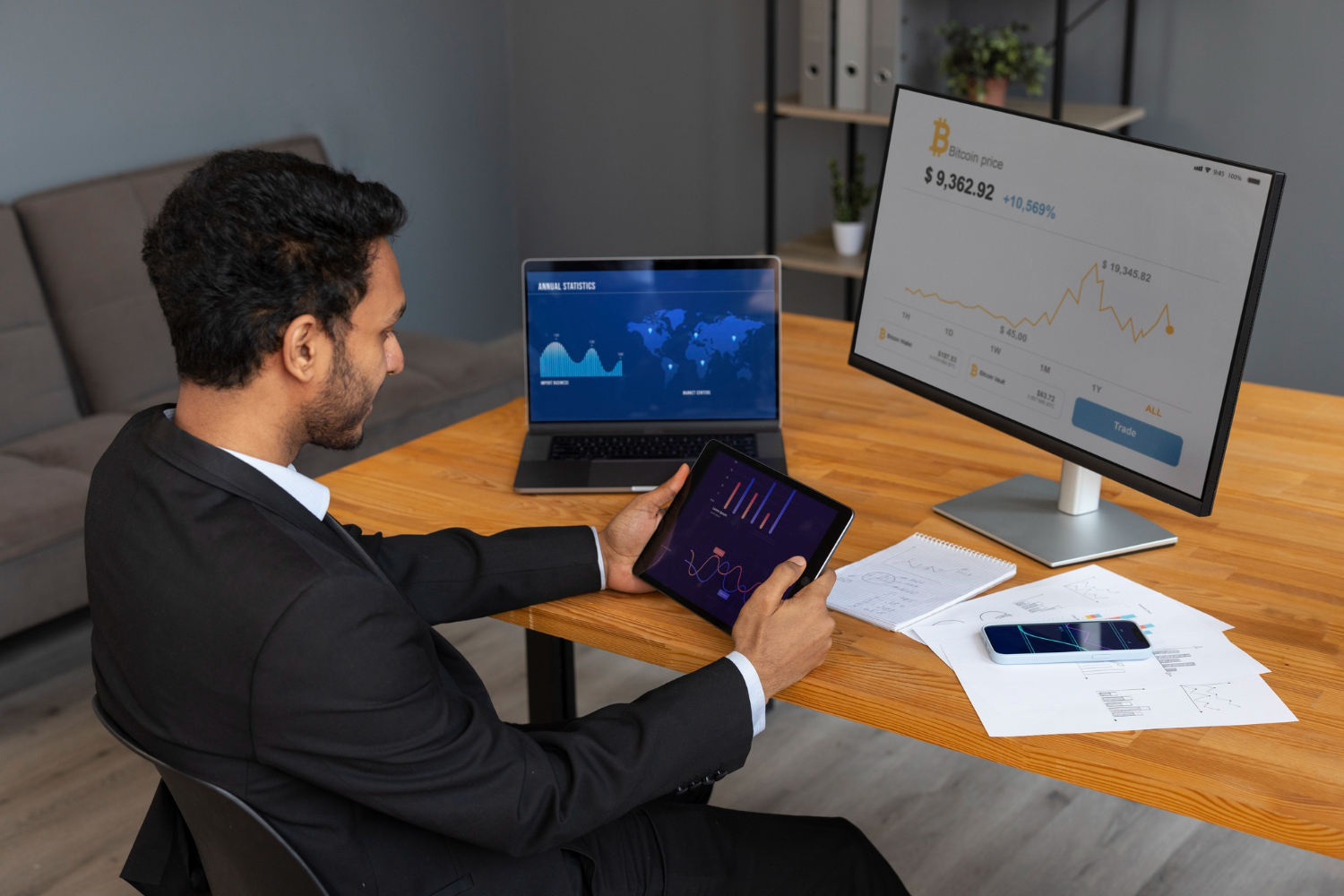

Implementing Financial Management in SAP Business One Cloud
- General Ledger:
- Comprehensive chart of accounts.
- Real-time financial data.
- Automated journal entries.
- Accounts Payable and Receivable:
- Streamlined invoicing and payments.
- Vendor and customer management.
- Aging reports.
- Banking and Reconciliation:
- Bank statement processing.
- Automated reconciliation.
- Cash flow management.
- Financial Reporting:
- Customisable financial reports.
- Real-time analytics.
- Integration with other business modules.
- Budget Management:
- Budget creation and tracking.
- Variance analysis.
- Financial forecasting.
- Accuracy and Efficiency:
- Automated processes reduce manual errors.
- Real-time data ensures accurate financial information.
- Cost Savings:
- Cloud deployment reduces IT infrastructure costs.
- Streamlined operations lower administrative expenses.
- Scalability:
- Easily adaptable to growing business needs.
- Flexible licensing options.
- Compliance and Security:
- Adherence to financial regulations and standards.
- Robust data security measures.
- Preparation and Planning
- Assess Current Systems:
- Evaluate existing financial management processes and systems.
- Identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Define Objectives:
- Set clear financial management goals.
- Determine key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Select a Project Team:
- Include stakeholders from finance, IT, and management.
- Assign roles and responsibilities.
- System Configuration
- Set Up Chart of Accounts:
- Define the structure of your general ledger.
- Customise account groups and hierarchies.
- Configure Financial Modules:
- Accounts payable and receivable.
- Banking and reconciliation.
- Integrate with Other Modules:
- Ensure seamless data flow between financial management and other business processes.
- Integration with sales, inventory, and CRM.
- Data Migration
- Prepare Data:
- Cleanse and validate existing financial data.
- Map data fields to SAP Business One Cloud.
- Migrate Data:
- Use data migration tools provided by SAP.
- Test data migration to ensure accuracy.
- User Training and Testing
- Train Users:
- Conduct training sessions for finance team members.
- Provide user manuals and support materials.
- Test the System:
- Perform thorough testing of financial processes.
- Validate financial reports and reconciliations.
- Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support
- Go-Live Preparation:
- Finalise system configuration and data migration.
- Communicate go-live plan to all stakeholders.
- Post-Implementation Support:
- Monitor system performance.
- Provide ongoing user support and training.
- Conduct regular system audits and updates.
- Regularly Review Financial Reports
- Monthly and Quarterly Reviews:
- Analyse financial statements regularly.
- Identify trends and variances.
- Automate Report Generation:
- Schedule automated reports.
- Use dashboards for real-time insights.
- Maintain Data Integrity
- Data Validation:
- Regularly audit financial data.
- Implement validation rules.
- User Access Control:
- Define user roles and permissions.
- Limit access to sensitive financial data.
- Optimise Cash Flow Management
- Monitor Cash Flow:
- Use cash flow forecasts and reports.
- Identify potential cash shortages.
- Improve Collections:
- Streamline invoicing and collections processes.
- Offer multiple payment options to customers.
- Enhance Budgeting and Forecasting
- Create Realistic Budgets:
- Base budgets on historical data and future projections.
- Adjust budgets as needed.
- Perform Variance Analysis:
- Compare actual performance against budgets.
- Investigate and address variances.
- Ensure Compliance
- Adhere to Accounting Standards:
- Implement GAAP or IFRS standards as required.
- Regularly update compliance practices.
- Conduct Regular Audits:
- Schedule internal and external audits.
- Address audit findings promptly.




 Applicable for Package
Applicable for Package Optional
Optional